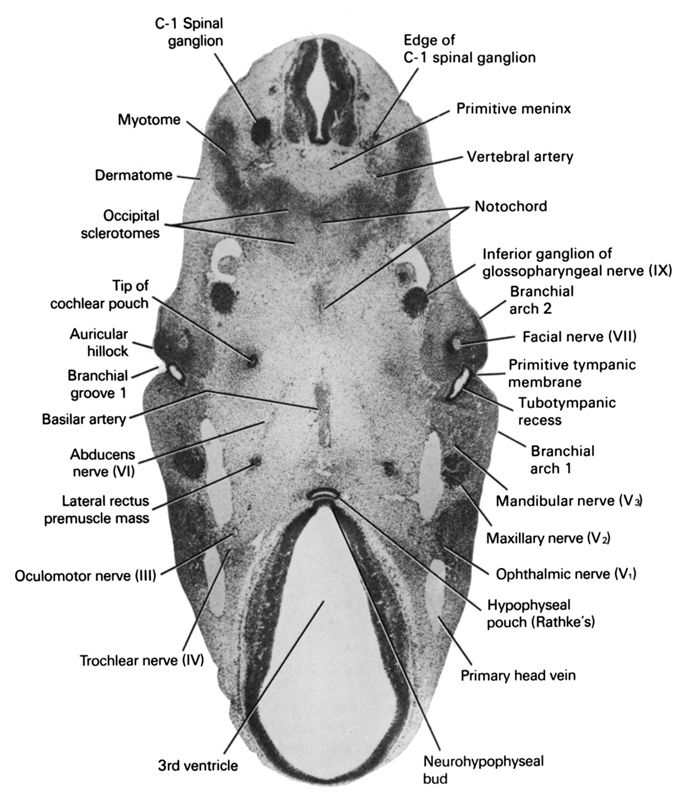
A section through the junction of the hypophyseal pouch with the neurohypophyseal bud.
Observe:
1. The three divisions of a somite: sclerotome, myotome and dermatome.
2. The basilar artery that travels in the midline on the ventral surface of the pons area in Section 8.
3. The abducens nerve passing to the lateral rectus premuscle mass.
4. The facial nerve in the middle of the second branchial arch.
5. The three divisions of the trigeminal nerve; ophthalamic, maxillary and mandibular nerves.
Keywords: C-1 spinal ganglion, abducens nerve (CN VI), auricular hillock, basilar artery, branchial arch 1, branchial arch 2, branchial groove 1, dermatome, edge of C-1 spinal ganglion, facial nerve (CN VII), hypophyseal pouch (Rathke's), inferior ganglion of glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), lateral rectus premuscle mass, mandibular nerve (CN V₃), maxillary nerve (CN V₂), myotome, neurohypophyseal bud, notochord, occipital sclerotomes, oculomotor nerve (CN III), ophthalmic nerve (CN V₁), primary head vein, primitive meninx, primitive tympanic membrane, third ventricle, tip of cochlear pouch, trochlear nerve (CN IV), tubotympanic recess (pharyngeal pouch 1), vertebral artery
Source: Atlas of Human Embryos.
