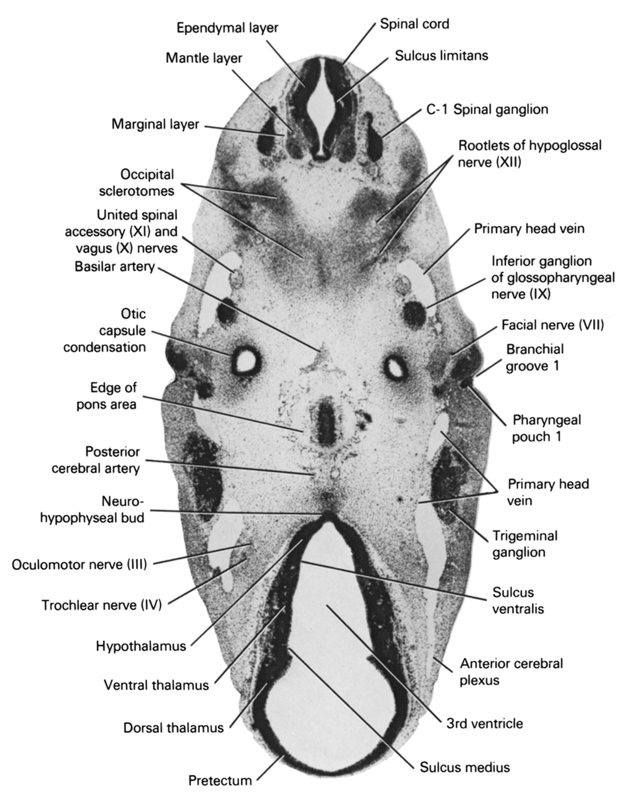
A section through the C-1 spinal ganglion, ventral edge of the pons area and neurohypophyseal bud.
Observe:
1. The fused occipital sclerotomes that contribute to skull formation around the hypoglossal nerve.
2. The inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
3. The close relation of the primary head vein to cranial nerves IX, X and XI and the trigeminal ganglion.
4. The dorsal part of the first branchial groove in contact with the first pharyngeal pouch in the ear area.
5. The sulcus medius between the dorsal thalamus and the ventral thalamus and the sulcus ventralis between the ventral thalamus and hypothalamus.
Keywords: C-1 spinal ganglion, anterior cerebral plexus, basilar artery, branchial groove 1, dorsal thalamus, edge of pons area, ependymal layer, facial nerve (CN VII), hypothalamus, inferior ganglion of glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), mantle layer, marginal layer, neurohypophyseal bud, occipital sclerotomes, oculomotor nerve (CN III), otic capsule condensation, pharyngeal pouch 1, posterior cerebral artery, pretectum, primary head vein, root of hypoglossal nerve (CN XII), spinal cord, sulcus limitans, sulcus medius, sulcus ventralis, third ventricle, trigeminal ganglion (CN V), trochlear nerve (CN IV), united spinal accessory (CN IX) and vagus (CN X) nerves, ventral thalamus
Source: Atlas of Human Embryos.
