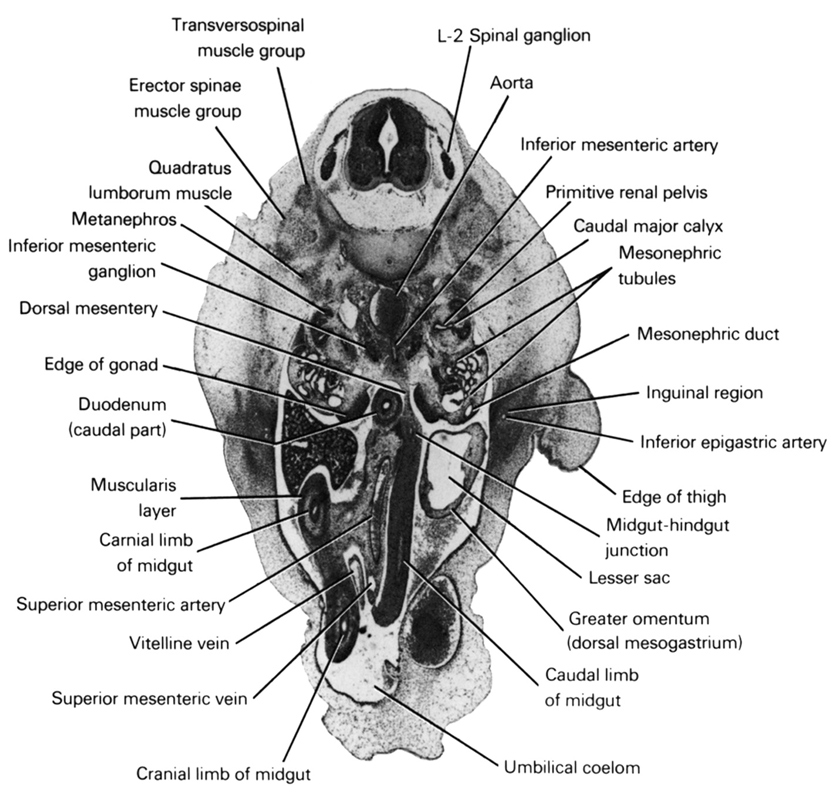
A section through the L-2 spinal ganglion and edge of the thigh.
Observe:
1. The extension of the peritoneal cavity into the umbilical cord to form the umbilical coelom that receives the herniated midgut.
2. The cranial limb of the midgut to the right of the caudal limb as a result of the counterclockwise rotation.
3. The mid- and hindgut junction near the midline in the dorsal mesentery.
4. The origin of the inferior mesenteric artery from the aorta.
5. The primitive renal pelvis medial to the metanephros where it gives rise to the caudal major calyx.
Keywords: L-2 spinal ganglion, aorta, caudal limb of midgut, caudal major calyx, cranial limb of midgut, dorsal mesentery, duodenum (caudal part), edge of gonad, edge of thigh, erector spinae muscle group, greater omentum (dorsal mesogastrium), inferior epigastric artery, inferior mesenteric artery, inferior mesenteric ganglion, inguinal region, lesser sac, mesonephric duct, mesonephric tubule(s), metanephros, midgut-hindgut junction, muscularis layer, primitive renal pelvis, quadratus lumborum muscle, superior mesenteric artery, superior mesenteric vein, transversospinal muscle group, umbilical coelom, vitelline (omphalomesenteric) vein
Source: Atlas of Human Embryos.
