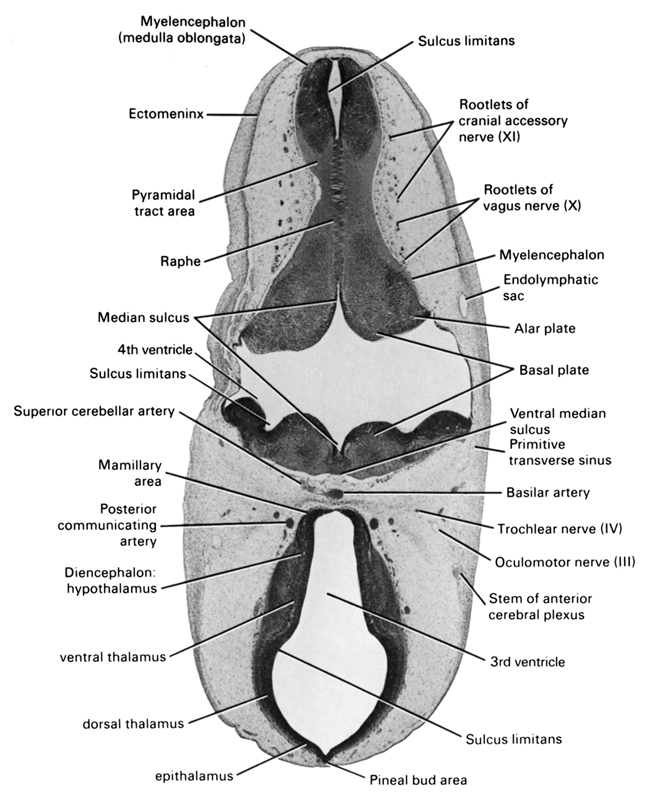
A section through the basal plate of the myelencephalon and caudal part of the diencephalon.
Observe:
1. The major subdivisions of the diencephalon and the continuity of the cerebral aqueduct in Section 5 with the third ventricle.
2. The median sulcus and sulcus limitans subdividing the floor of the fourth ventricle.
3. The close relationship of the endolymphatic sac to the roof of the fourth ventricle.
4. The midline raphe in the ventral part of the myelencephalon produced by crossing fibers.
5. The rootlets of the vagus and cranial accessory nerves that arise from the ventrolateral surface of the myelencephalon.
Keywords: alar plate(s), basal plate, basilar artery, diencephalon hypothalamus, dorsal thalamus, ectomeninx, endolymphatic sac, epithalamus, mamillary area, median sulcus, myelencephalon, myelencephalon (medulla oblongata), oculomotor nerve (CN III), pineal bud area, posterior communicating artery, primitive transverse sinus, pyramidal tract area, raphe, rhombencoel (fourth ventricle), root of cranial accessory nerve (CN XI), root of vagus nerve (CN X), stem of anterior cerebral plexus, sulcus limitans, superior cerebellar artery, third ventricle, trochlear nerve (CN IV), ventral median sulcus, ventral thalamus
Source: Atlas of Human Embryos.
