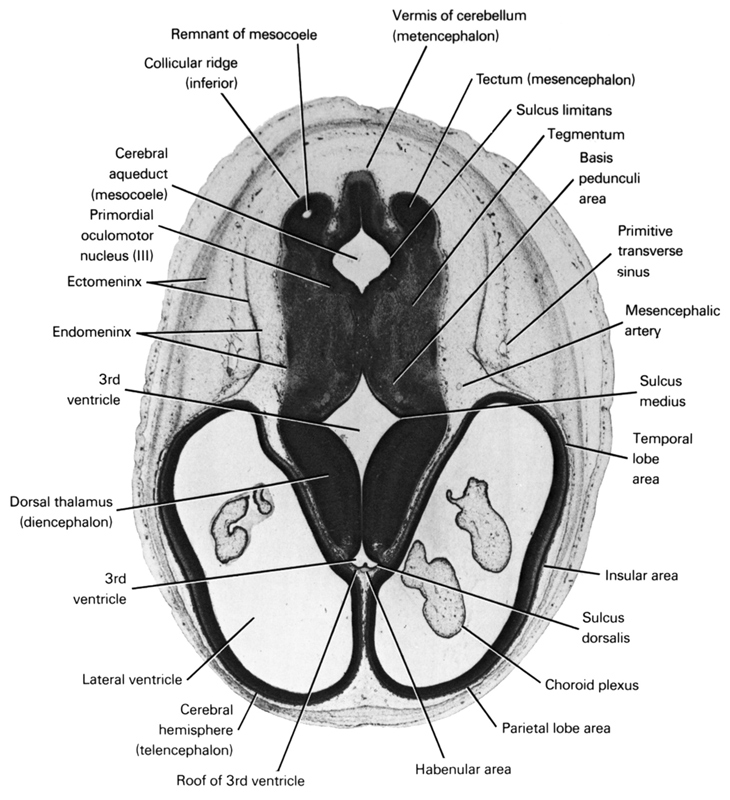
A section through the cerebral hemisphere (parietal and temporal lobe areas), dorsal thalamus and basis pedunculi area, tegmentum and tectum of the mesencephalon.
Observe:
1. The choroid plexus in the lateral ventricle.
2. Two areas of the third ventricle in the midline at the level of the diencephalon.
3. The narrowed segment of the mesocoele where the cerebral aqueduct begins to form.
4. The caudal part of the collicular ridge in the tectum on each side of the cerebellar vermis.
5. The primordial nucleus of cranial nerve III in the tegmentum.
Keywords: basis pedunculi area, cerebral aqueduct (mesocoel), cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon), choroid plexus, collicular ridge (inferior), dorsal thalamus (diencephalon), ectomeninx, endomeninx, habenular area, insular area, lateral ventricle, mesencephalic artery, parietal lobe area, primitive transverse sinus, primordial oculomotor nucleus, remnant of mesocoele, roof of third ventricle, sulcus dorsalis, sulcus limitans, sulcus medius, tectum of mesencephalon, tegmentum, temporal lobe area, third ventricle, vermis of cerebellum (metencephalon)
Source: Atlas of Human Embryos.
