Prenatal Form and Function – The Making of an Earth Suit
Unit 3: 2 to 3 Weeks
 Closer Look:
Closer Look:
 Applying the Science:
Applying the Science:
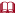
Germ Layers
By about 15 days (2 weeks, 1 day) following fertilization, stem cells have divided and differentiated into three different germ layers called ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. Each gives rise to major components of specific body structures and organs.1 (See Figure 3.2 below.)
Ectoderm derivatives include the skin, nails, hair follicles, sweat glands, and nerves within the lungs.2 Another specialized layer of cells appearing at this time is the neuroectoderm, which gives rise to the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, as well as many of the muscles and bones in the face.3
Endoderm forms the lining of the respiratory4 and gastrointestinal tracts and gives rise to major portions of internal organs including the lungs, liver, pancreas, and intestines.5
Mesoderm derivatives include the heart, kidneys, bones, muscles, and blood vessels as well as portions of the reproductive and urinary systems.6
Mesoderm also gives rise to specialized cells called somites (so’mits).7 These cells form most of the skull and ribs as well as the vertebral column or backbone.8
All of these cell layers and cell types work in concert forming the increasingly complex embryo.

Copyright © 2002 Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins.
All rights reserved.



All rights reserved.



Copyright © 2002 Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins.
All rights reserved.
By day 17 the central portion of the thyroid gland appears.9 This important gland will soon regulate the rate of metabolism throughout the rest of the human life cycle.
The embryo’s respiratory system begins to develop by 3 weeks with an outgrowth of the foregut which will form the windpipe or trachea (tra’ke-a).10
The Brain & Spinal Cord - Early Emergence
The site of future brain development is first recognizable with the appearance of the neural plate by 2 weeks, 4 days. By 3 weeks the neural plate thickens first at the head end of the embryo and folds into the neural tube which will form the brain and the spinal cord.11 By 3 weeks, the 3 primary sections of the brain are identifiable. These sections are called the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.12
Vital Systems – Circulation
The complexity achieved by the embryo in just the first 3 weeks of development is incredible. Considering the importance of distributing nutrients to the emerging brain and spinal cord, as well as the rest of the embryo, the early development of the circulatory system is not surprising.

Copyright © 2002 Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins.
All rights reserved.
Yet the early completion of this body system – the first system to begin functioning – is remarkable.13 By 3 weeks early blood cell precursors appear in the yolk sac.14 This process of blood cell formation is called hematopoiesis. Also by 3 weeks, early blood vessels form throughout the embryo as the network of the early circulatory system begins to take shape.15
In the middle of week 3, only 18 days after fertilization, the embryo’s heart appears.




