Prenatal Form and Function – The Making of an Earth Suit
Unit 7: 6 to 7 Weeks
 Closer Look:
Closer Look:
 Applying the Science:
Applying the Science:
Copyright © 2006 EHD, Inc. All rights reserved.
The embryo has brainwaves by 6 weeks, 2 days!
From 6 to 6½ weeks, the cerebral vesicles will double in size.1 Individualized brainwaves recorded via electroencephalogram (e-lek’tro-en-sef’a-lo-gram), or EEG, have been reported as early as 6 weeks, 2 days.2
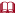
Also by 7 weeks, cell groupings resembling taste buds appear on the tongue3 and hiccups begin.4 Nasal plugs are prominent at this time and will persist for another 6 weeks or so.
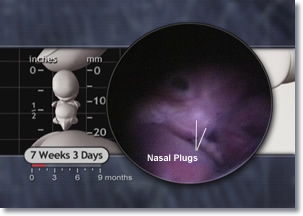
By 7 weeks, the heart has 4 chambers.5
The pacemaker center is already well-established in the right atrium.6 The embryonic heart rate peaks at 7 weeks and now beats approximately 167-175 times per minute.7 This rate gradually declines to about 140 beats per minute at birth.8
Copyright © 2002 Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins.
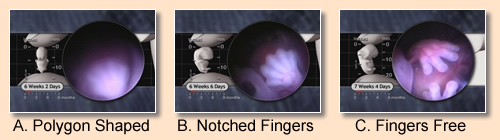
By 6½ weeks, the elbows are distinct and the embryo begins moving both hands. The fingers are also starting to separate as evidenced by the appearance of notching between the digital rays.9
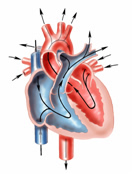
The foot plate and ankle also emerge while toes and metatarsal (met’a-tar’sal) bones begin to form in the feet. Joint development is underway10 and the onset of primary muscle fiber formation indicates the embryo’s muscles are growing.11

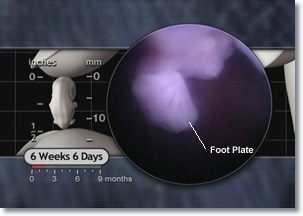
Copyright © 2006 EHD, Inc. All rights reserved.
The hands and feet change dramatically between 6 and 7 weeks as separate fingers and toes begin to emerge. At 6 weeks the hand plates develop a subtle flattening between the digital rays. By 6 weeks, 2 days the hand takes on a polygon shape; prominent notches appear between the digital rays by 7 weeks and individual fingers are fully separated by 7½ weeks.12
Copyright © 2006 EHD, Inc. All rights reserved.
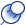
Bone formation begins between 6 and 7 weeks, starting with the clavicle, or collar bone, and the upper and lower jaw. This process is called ossification.13
No Bones About It

Ossification is the process by which bones harden. But how does it happen? Basically, either existing membranes or cartilage (that firm connective tissue found in your ears and the tip of your nose) begin to harden through repeated deposits of calcium and phosphorus. Cells called osteoblasts form a bony framework. Osteoblasts then produce enough small chunks of bone to cover this framework, creating a solid bone.
Dairy products and many dark green veggies (such as spinach) are high in calcium which helps build bones providing the shape and structure of our body.
- Stedman's Medical Dictionary, Ed. Marjory Spraycar, et al., 26th ed. (Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1995), 1266.
- Keith L. Moore and T. V. N. Persaud, The Developing Human, Clinically Oriented Embryology, 6th ed. (Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders, 1998), 408-411.

Also, by 7 weeks, the embryo moves the legs and exhibits a startle response.14


The immune system is maturing, as evidenced by the presence of B-lymphocytes in the liver.15 After birth and relocation away from the protection of the womb, these lymphocytes will produce proteins called antibodies to fight infection.
By 7 weeks, the ovaries appear in the female embryo.16 In the male embryo, a gene on the Y-chromosome produces a substance causing the testes to begin to differentiate.17










